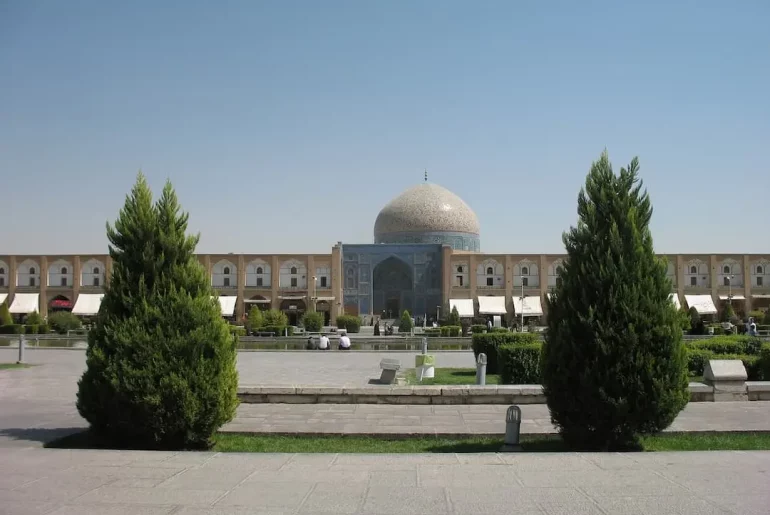
Persian architecture is famous for its captivating and grand design, incorporating various cultural influences and indigenous craftsmanship. Dating back to ancient times, it showcases meticulous attention to detail with delicate ornaments adorning structures like palaces, mosques, and gardens. The vibrant colors and intricate geometrical patterns enhance its magnificence. Persian architects seamlessly incorporate nature into their designs, creating a harmonious connection between built environments and the natural world—the results in tranquil spaces with flourishing gardens and flowing water elements. Persian architecture continues to captivate admirers worldwide through its striking aesthetics and thoughtful design principles.
Historical background: Tracing the origins of Persian architectural marvels

The Persian architectural marvels originated in the ancient Achaemenid Empire, from 550 BCE to 330 BCE. Emperors such as Cyrus the Great and Darius I revolutionized architecture with grand palaces, massive columns, and intricate stone carvings. These structures showcased artistic beauty and functionality, employing advanced engineering techniques and mathematical calculations. Subsequent dynasties like the Parthians and Sassanids continued this tradition. At the same time, the Islamic period saw the zenith of Persian architecture with iconic structures like Isfahans Jameh Mosque and Tehrans Golestan Palace. Meticulous craftsmanship, attention to detail, and structural stability have preserved these marvels, serving as a testament to Persia’s historical legacy and inspiring architects globally.
Key features: Examining the unique elements that define Persian architecture
Persian architecture showcases the remarkable craftsmanship and design principles of ancient Persian architects. One key feature is intricate tile work called Kashi, which utilizes durable tiles arranged in symmetrical patterns to create visually striking facades. The use of arches, particularly the iwan, adds grandeur to entrances and offers glimpses into surrounding courtyards; it also emphasizes the integration of gardens, known as baghs, incorporating natural elements for a harmonious blend of humans and nature. Combining artistry, science, spirituality, and cultural identity has created enduring masterpieces.
5 Iconic landmarks: Showcasing famous Persian architectural wonders
Persian architecture boasts a rich heritage, with five iconic landmarks showcasing its brilliance
1. Persepolis

This ancient city represents the pinnacle of Persian architectural achievement. Its grandiose palaces, colossal gateways, and intricate stone carvings tell the Achaemenid Empire’s glory story.
2. Isfahan’s Imam Mosque

Known for its stunning blue-tiled mosaics and remarkable acoustics, this mosque exemplifies Persian Islamic architecture, blending beauty with functionality.
3. Tomb of Cyrus the Great
Located in Pasargadae, this mausoleum is a testament to simplicity and elegance. Its architectural purity reflects the ethos of the Persian civilization’s founder.
4. Nasir al-Mulk Mosque
Located in Shiraz, this “Pink Mosque” is renowned for its stained glass window kaleidoscope, creating a mesmerizing play of colors and light.
5. Windcatcher Towers of Yazd

These ancient structures demonstrate Persian ingenuity in passive cooling systems. The windcatchers harness the desert breeze to provide natural ventilation in the arid city of Yazd.
Islamic influence: Exploring the fusion of Islamic and Persian architectural styles
Islamic architecture in Persia blends seamlessly with Persian architectural styles, resulting in awe-inspiring structures that reflect Islamic principles and Persian spatial concepts. Elements such as domes, minarets, and intricate floral motifs showcase this fusion. Islamic influence introduced pointed arches and geometric patterns, while Persian designs retained symmetry. The use of geometry symbolizes the universe’s interconnectedness in Islamic culture, and calligraphy featuring Quranic verses adorns the architecture. These marvels demonstrate the integration of Islamic artistic expressions in local contexts through centuries of cultural exchange.
Intricate tilework: Discussing the mesmerizing beauty of Persian mosaic patterns
Persian tilework is a breathtaking art form that combines precise mathematics with artistic expression. Each tile is carefully crafted by hand and assembled into intricate patterns that flow seamlessly. The vibrant hues intensify the visual appeal and instill a sense of vitality. These mosaics showcase stunning designs and share stories from Persian history and mythology. They have been adorned in palaces and public buildings for centuries, standing the test of time. Today, they continue to captivate audiences worldwide, showcasing the exceptional skills of Persian artisans throughout history.
Structural innovations: Unveiling the engineering brilliance behind Persian domes and arches
Persian architecture is known for its structural innovations, particularly in domes and arches. One notable technique was squinch, Enabling a seamless shift from a square foundation to a rounded dome. They have ensured stability and strength while maintaining aesthetic appeal. Persian architects also incorporated intricately designed arches, supported by ribbed vaults, to increase height and create open spaces without compromising structural integrity. These architectural marvels reflect ancient Persian engineers’ advanced knowledge and skill, leaving a lasting legacy of excellence.
Preservation efforts: Shedding light on initiatives to safeguard these timeless masterpieces
Preservation efforts are crucial in safeguarding timeless masterpieces for future generations. These initiatives involve preventing deterioration, restoring damaged artifacts, and raising awareness about preservation needs. Conservation experts use scientific methods and advanced technologies to assess artwork conditions and develop effective maintenance strategies.
Environmental conditions, handling procedures, and storage techniques are carefully considered to minimize risks. Collaboration between museums, galleries, labs, and educational institutions is vital for successfully preserving and sharing expertise and resources. Public engagement initiatives educate visitors on proper art appreciation practices and the importance of responsible stewardship. Without these efforts, our cultural heritage would risk irreparable loss.
Contemporary inspirations: Examining how Persian architecture continues to influence modern design
Persian architecture is known for its unique characteristics and intricate craftsmanship, inspiring contemporary design. Elements such as geometric patterns, elegant arches, and vibrant colors are still widely used by architects and designers worldwide. Modern design also draws inspiration from the harmony between buildings and nature in traditional Persian gardens, with their symmetrical layout and serene atmosphere. The use of ornate tiling, both indoors and outdoors, reflects the lasting impact of Persian architecture on modern aesthetics. The attention to beauty, functional forms, and integration with nature in Persian architecture continues to shape today’s architectural landscapes.
Conclusion
The lasting impact of Persian architecture showcases the brilliance of ancient Persia, displaying remarkable creativity, technical talent, and cultural significance. From breathtaking structures like Persepolis and Isfahans Imam Mosque to intricate decorative motifs in palaces and mausoleums, Persian architecture has fascinated scholars and art enthusiasts for centuries. Contemporary designers continue to draw inspiration from these timeless aesthetics and innovative engineering techniques.
Persian design combines form and function seamlessly with a profound understanding of proportion, symmetry, light, and space. Beyond their beauty, these buildings also reflect ancient Persia’s rich history, religious beliefs, and societal values. Reflecting on this enduring legacy helps us appreciate its contributions to human history and emphasizes the importance of preserving these unmatched works of art for future generations.